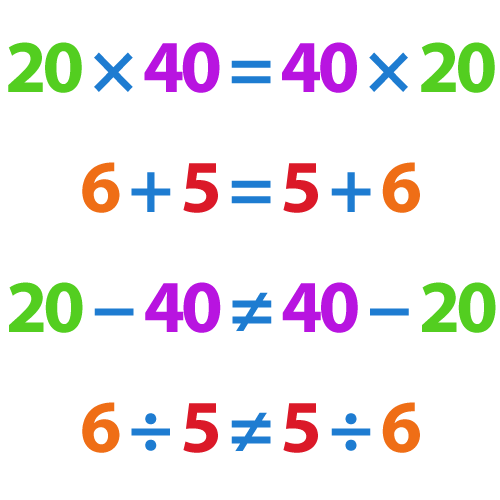commutative
This is a law which is used to describe mathematical operators that give the same answer, even if the order in which we input the numbers are changed.
The addition and multiplication of numbers are commutative, i.e.
-
a + b = b + a
a × b = b × a
For example:
-
2 + 3 = 3 + 2
2 × 3 = 3 × 2
The answers to the above are the same.
The subtraction and division of numbers are not commutative.
For example:
-
2 – 3 ≠ 3 – 2
2 ÷ 3 ≠ 3 ÷ 2
The answers to the above are not the same, therefore the ≠ sign is used to show this.