Pythagoras’ theorem
Pythagoras’ theorem is a mathematical theorem for a right-angled triangle.
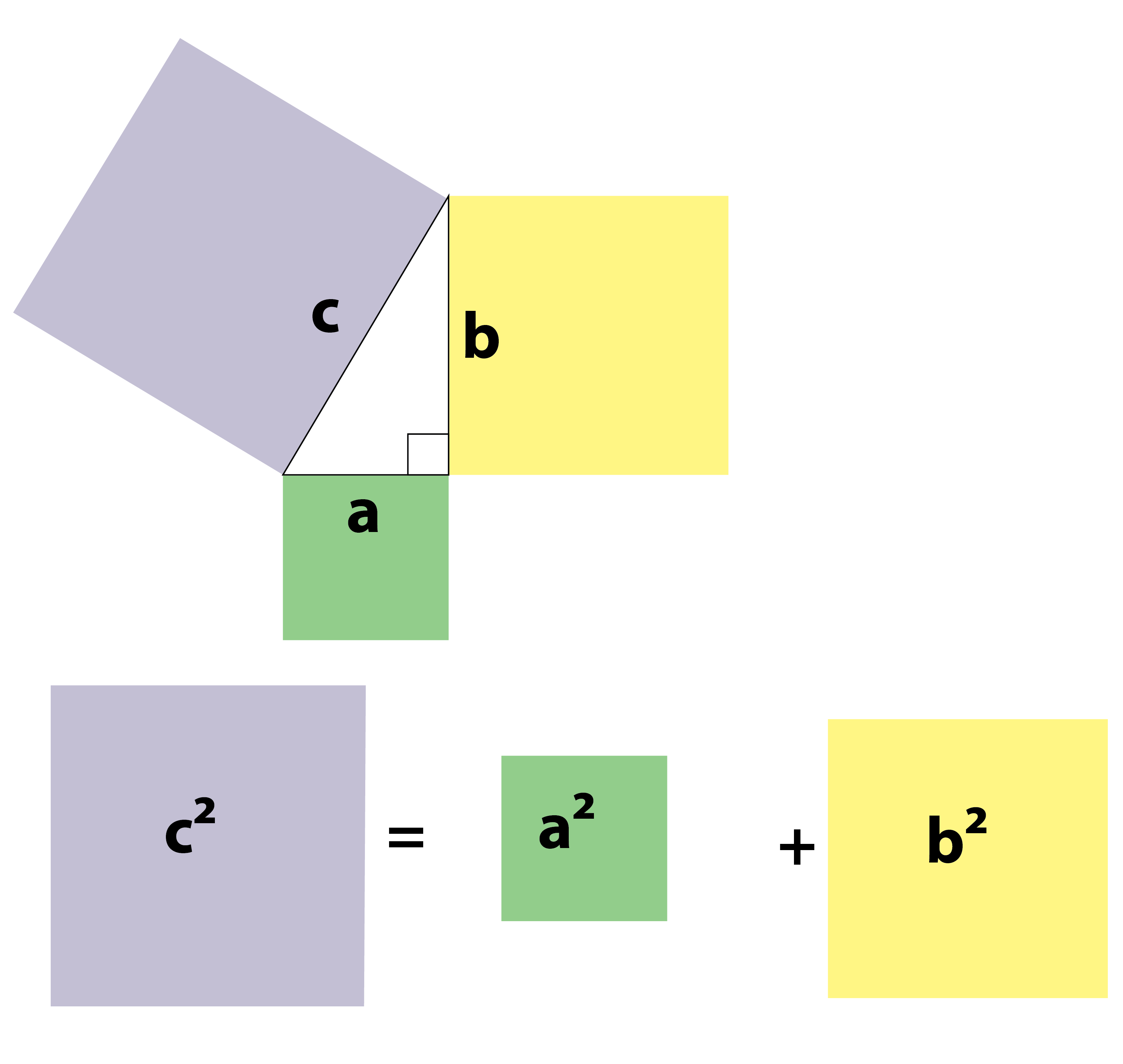
The area of the square on the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the total area of the squares on the other two sides of the triangle.
We write Pythagoras’ theorem in the form of a² + b² = c². The a, b and c refer to the length of the sides of a right-angled triangle as shown in the diagram.