cosine rule
The cosine rule is used to discover the length of a missing side or the size of a missing angle in a triangle. It can be a right-angled triangle or a triangle with no right angles.
The rule is based on the relationship between two sides of a triangle and the angle between those sides.
The rule has two forms:
(1) To discover the length of a side:
![]()
![]()
![]()
(2) To discover the size of an angle:
![]()
![]()
![]()
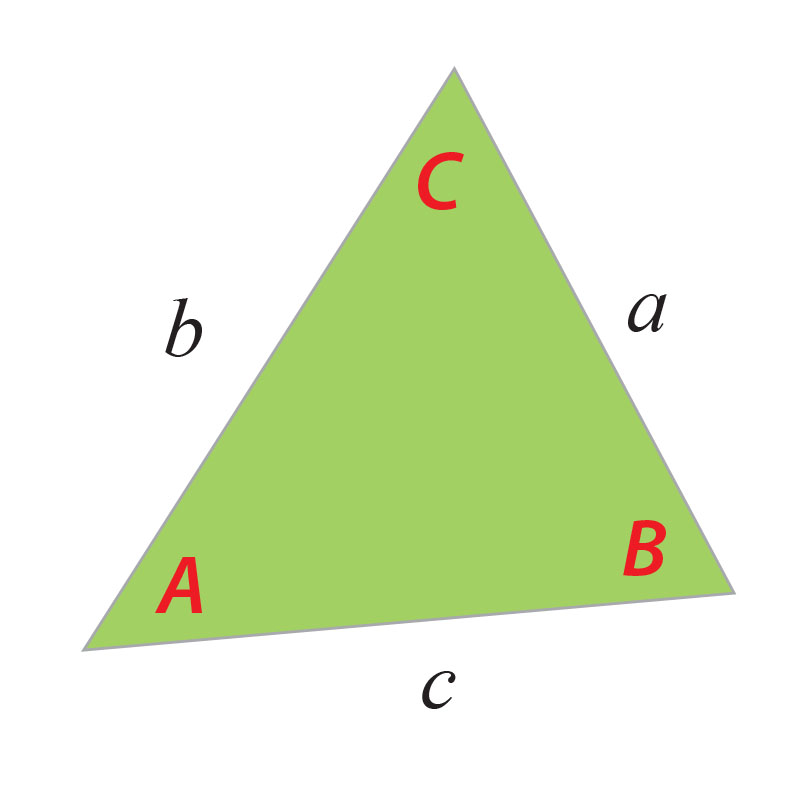
The letters a, b, c refer to the sides of the triangle, and the letters A, B, C refer to the angles of the triangle that are opposite the sides a, b, c.