relative frequency
Following an experiment, test or survey, we can use results to estimate probability.
We do this by using the following formula:
The term for the estimate of the probability is relative frequency.
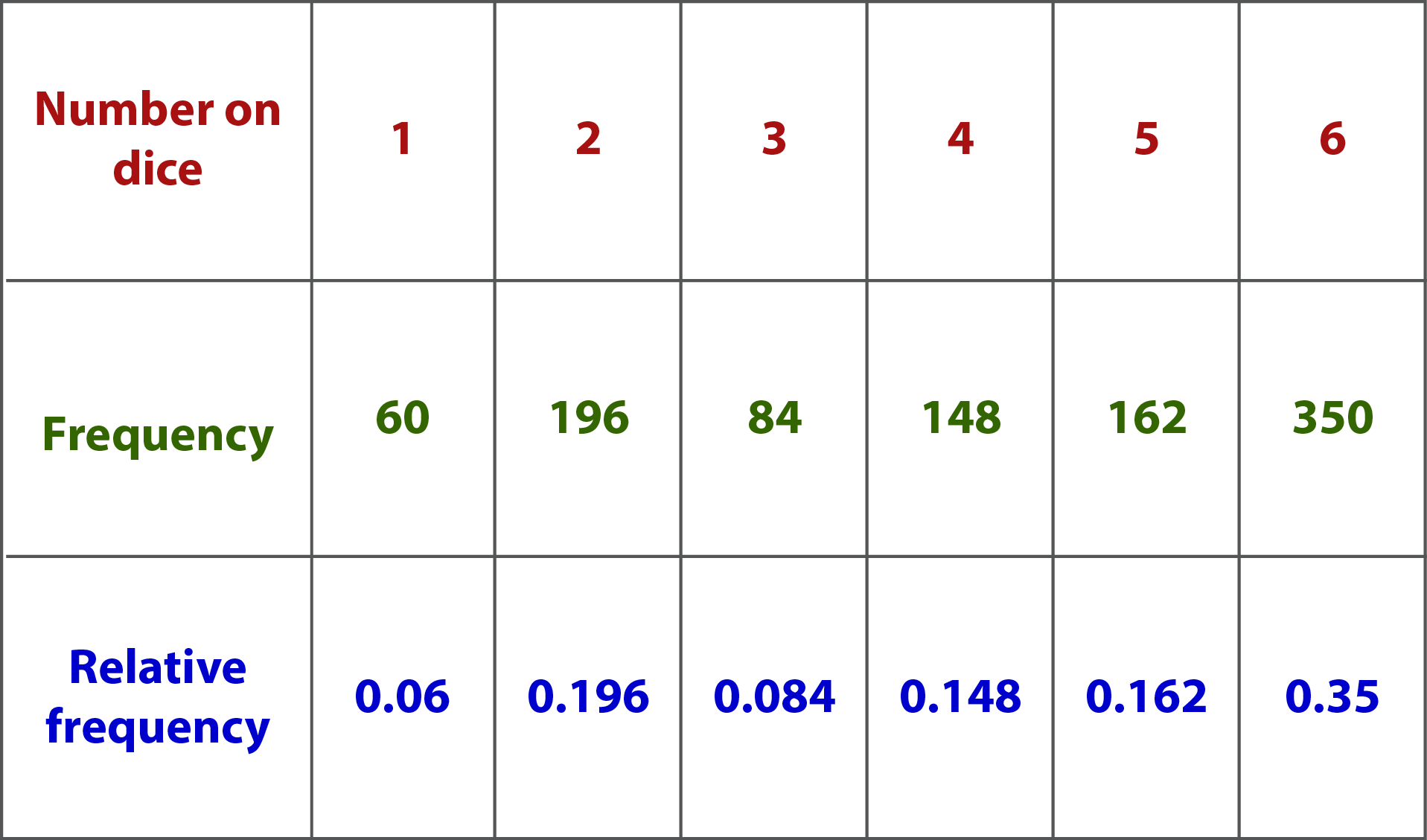
The table shows the results of throwing a dice 1000 times.
We can use these results to estimate the probability of getting a 6 each time the dice is thrown.
During 1000 throws, 6 has appeared 350 times.
In order to calculate the relative frequency, we must divide the number of times 6 has appeared, which is 350, by the number of trials, which is 1000. Therefore, the relative frequency of throwing a 6 is 350 ÷ 1000 = 0.35.