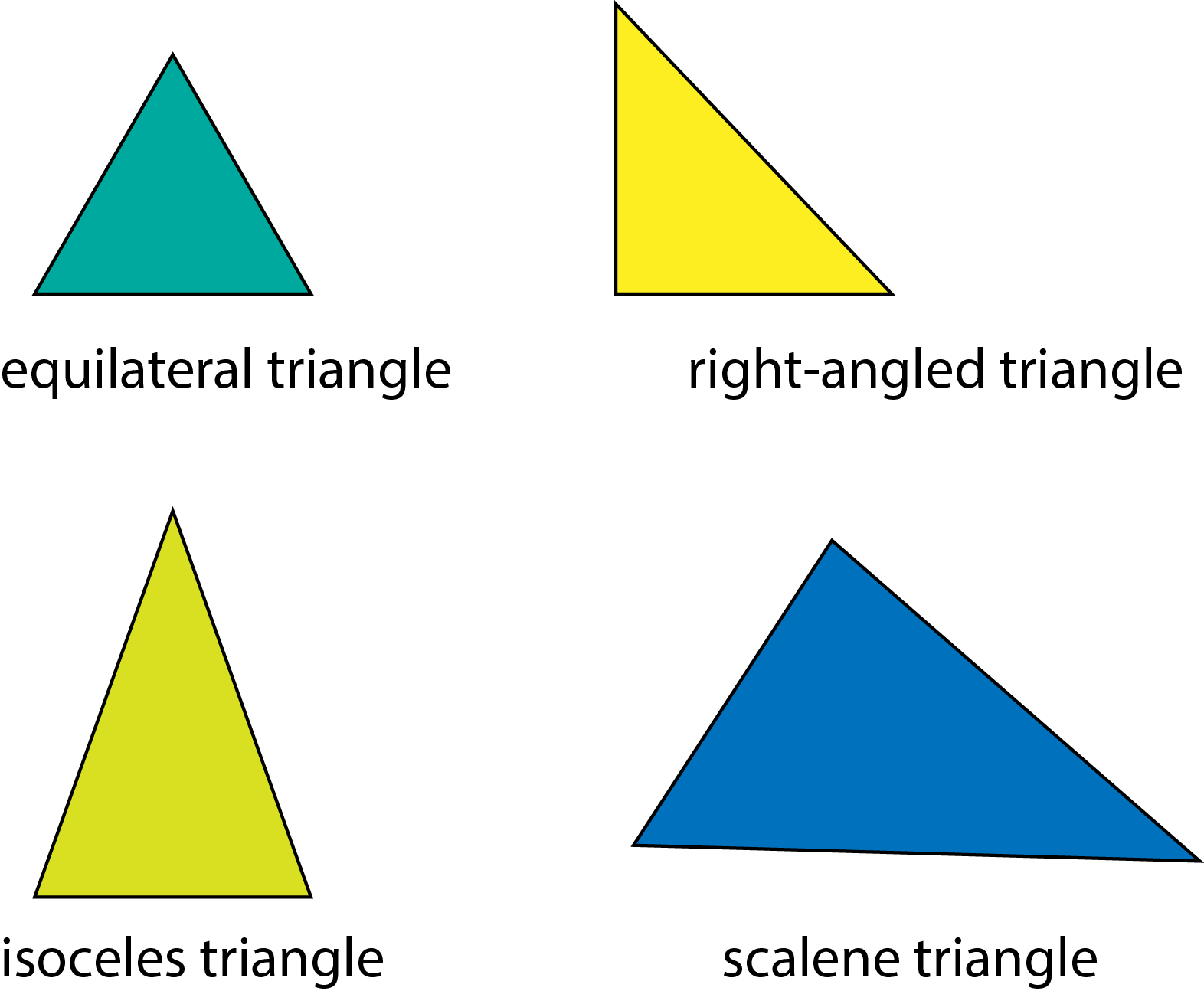triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three vertices and three sides.
There are different types of triangles:
-
• equilateral
• scalene
• right-angled.
The interior angles of any given triangle add up to a total of 180°.
There are two formulas for calculating the area of a triangle. One formula is:
![]()
The base b represents the length of one of the triangle’s sides and the height h represents the distance from the base to the opposite vertex. Note that the height is measured at a right angle to the base.
The other formula is:
In this formula a and b represent the length of two of the triangle’s sides and C represents the angle between these sides.
It is possible to use several methods to decide whether two triangles are similar or congruent.
If we have a right-angled triangle, we can use Pythagoras’ theorem or trigonometry methods to discover missing lengths or angles.
In a triangle with no right angles, we can use the sine rule or the cosine rule to discover missing lengths or angles.